Looking Good Tips About How To Tell If A File Is Hard Link

Organize your side hustle income.
How to tell if a file is a hard link. And if you don't finish everything right away, that's ok. Hard links work because of how unix handles files: If the given file is called /path/to/file and you want to find all hard links to it that exist under the current directory, then use:
Hard links can only be created for files. I had an idea that unfortunately doesn't work:. However, finddupe can only find instances of the hardlinked file.
In this mode, finddupe will list which groups of files are hardlinked together. If two or greater it is a hardlinked file. If the original file is deleted, the data still exists under the secondary hard link.
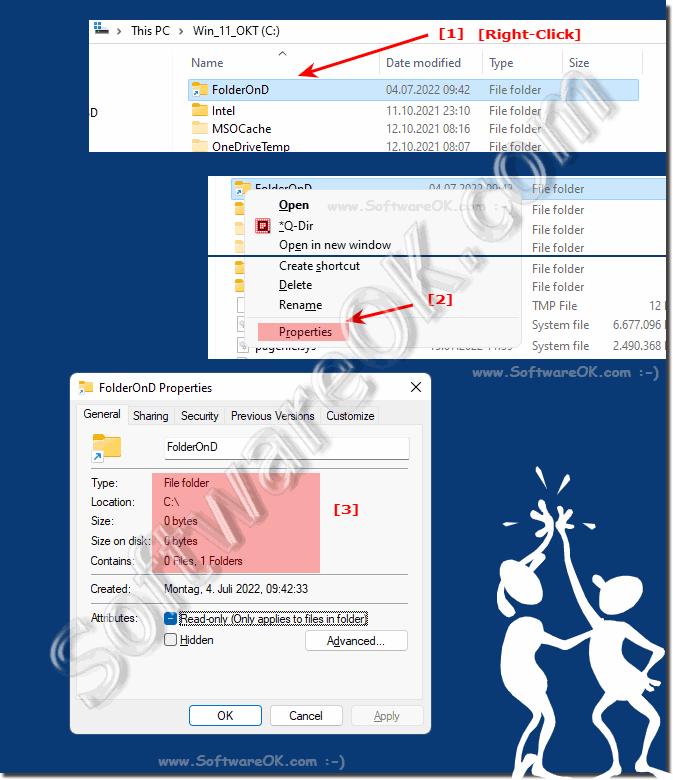
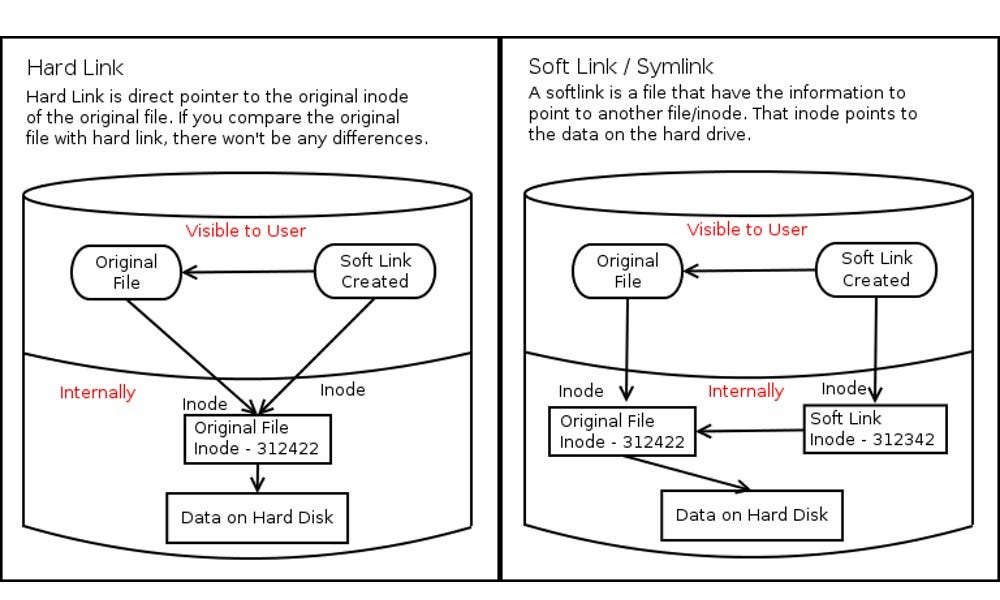
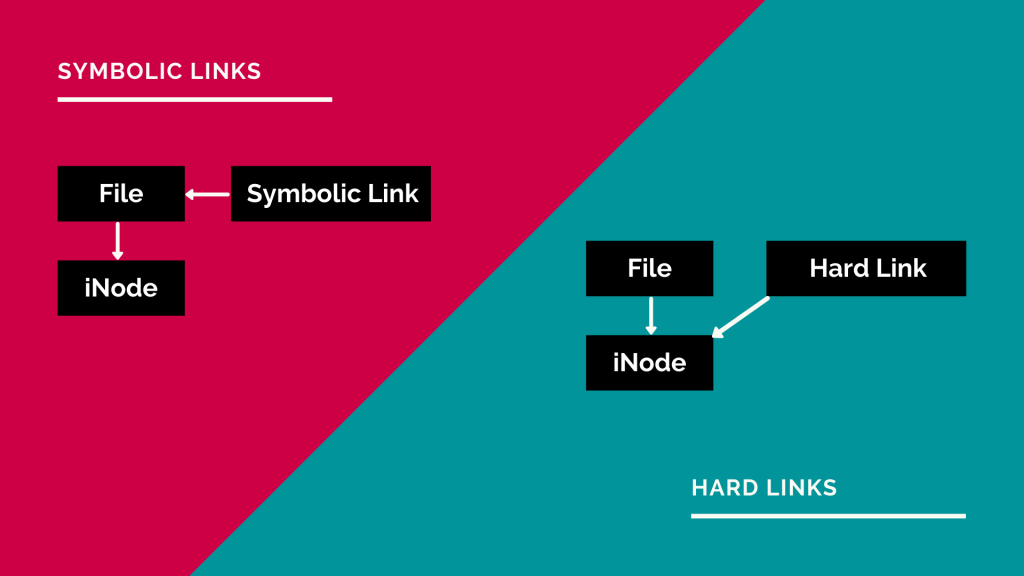
Each file is represented by a single inode. The data is only removed from your drive when all links to the data have been. Then a single inode has zero or more names or directory entries or, technically,.
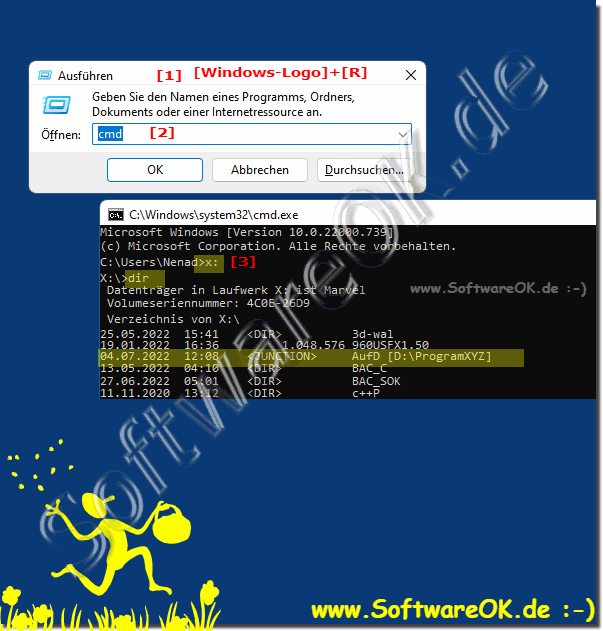
60 the fsutil utility included in windows xp and higher. You can of course change the directory the search starts from by changing the c:\windows\system in the command. Most tax filing software makes picking up where you left off easy.
For example, let’s compare the files, file_a, and file_b to check whether they are hard links: 6 answers sorted by: How do you check whether a file is a hard link in go?
Symlinks can point to relative paths (eg./parent.file) by extension, if you move the. Any changes to that file are instantly visible to applications that access it through the hard links that reference it. All hardlinked instances found of a file are shown together.
Then a single inode has zero or more names or directory entries or,. Each file is represented by a single inode. Os.filemode only has a mode for symlinks, not hard links.
Fsutil.exe hardlink list c:\windows\system32\notepad.exe sample results (from. I know that you can do: If i've created a directory link via mklink, how can i figure out if it was a symbolic link, a directory.


-Step-5.jpg)









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HgEtP6I7N6-e854a772e6d042ce994ec03fe9c40212.png)

